A website’s success isn’t just about having great content or a stunning design. How your content is organized and structured behind the scenes can make a big difference. One crucial element that often gets overlooked is the way URLs are structured. The organization of your URLs not only affects how search engines crawl your site but also plays a role in how users interact with it. A well-thought-out URL structure can significantly enhance your site’s SEO performance. When implemented correctly, an SEO-friendly URL structure helps improve visibility, makes navigation easier, and strengthens your site’s credibility. Understanding the importance of URL structure SEO is the key to optimizing your website for both users and search engines.
What is the URL?
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the web address used to identify a specific resource on the internet. It provides a way for users to access websites and their content by specifying a location on the web. Essentially, a URL acts as the address that directs browsers to the exact page or file you want to view. A URL consists of several key components, including the protocol (like HTTP or HTTPS), the domain name (such as www.example.com), and the path (which can point to a specific page or resource).
In simpler terms, the URL is the specific web address that takes you to a webpage, image, video, or other types of online content. For instance, the URL https://www.example.com/about-us directs you to the “About Us” page of a website. URLs are crucial for navigating the web and play a significant role in ensuring that search engines can index and retrieve web pages correctly.
Example of URL:
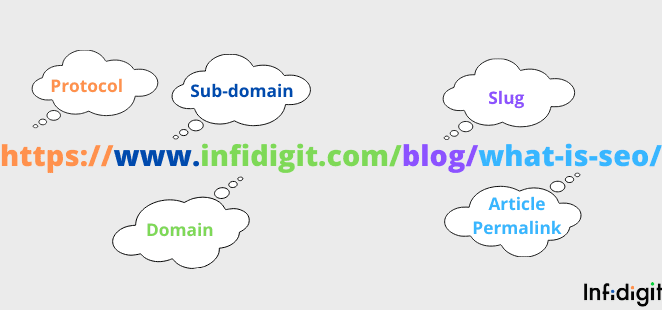
An example of a URL is https://www.infidigit.com/e-commerce-seo/. This URL is structured to guide both users and search engines to a specific page on the Infidigit website.
- Protocol: https signifies that the connection is secure, ensuring safe data transmission.
- Domain Name: www.infidigit.com is the unique address for the Infidigit website.
- Path: /e-commerce-seo/ directs users to a page dedicated to E-commerce SEO services.
In this example, the URL clearly communicates the page’s content, which is focused on E-commerce SEO, making it easy for both users and search engines to understand what the page offers. The clean structure helps in both user experience and SEO optimization.
What is the URL structure?
URL structure refers to the way a URL is organized to direct users and search engines to specific content on the web. It involves the arrangement of different components that make up a URL, such as the domain name, path, and other optional elements. A clean and logical URL structure enhances both the user experience and SEO by making it easier for people to navigate your site and for search engines to understand the content of your pages. Proper URL structure helps in improving site organization, visibility, and accessibility.
Protocol (HTTP or HTTPS)
The protocol specifies the method used to access the resource on the web. It tells the browser how to communicate with the web server. The most common protocols are HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure). HTTPS is the secure version of HTTP, encrypting the data exchanged between the browser and the website to ensure privacy and security.
Example: https://www.infidigit.com (The https indicates that the site is secure, offering a safe browsing experience.)
Subdomain
A subdomain is a part of the main domain and is used to organize and categorize content on a website. It allows businesses to create distinct sections under their primary domain. Subdomains can be used for blogs, customer portals, or separate business functions like e-commerce.
Example: www.infidigit.com (Here, www is a subdomain that points to the main homepage of the Infidigit website.)
Domain
The domain is the primary address of your website and identifies your site on the internet. It is the unique name that users type into the browser to access your website. Domains are typically purchased through domain registrars.
Example: www.infidigit.com (In this case, infidigit.com is the domain name, representing the Infidigit website.)
Domain Extension
The domain extension is the last part of the domain name, following the dot (.). Common extensions include .com, .org, .net, and more. The domain extension helps categorize the type of website, such as commercial, non-profit, or network-related sites.
Example: www.infidigit.com (Here, .com is the domain extension, commonly used for commercial websites.)
Subdirectory
A subdirectory is a folder within your website’s root directory that helps organize content or separate different sections of your site. It is part of the URL path and can be used for various purposes, such as blog posts, services, or product categories.
Example: www.infidigit.com/blog (In this URL, /blog is a subdirectory where the blog content is located within the Infidigit site.)
Path
The path in a URL points to the specific location of a file or page on the server. It is the section of the URL that comes after the domain and subdirectory, providing detailed navigation to a specific resource.
Example: www.infidigit.com/blog/what-is-seo (Here, /blog/what-is-seo is the path leading to the “What is SEO” blog page on Infidigit’s website.)
Fragments
A fragment refers to a specific section within a webpage, typically after a hash (#) symbol. It helps users navigate directly to a part of the content on a page without having to scroll.
Example: www.infidigit.com/blog/what-is-seo/#seo-blog-tips (In this URL, #seo-blog-tips directs the user to the “SEO Blog Tips” section within the Infidigit blog.)
Query
A query is a part of the URL that allows you to send data to the web server, often in the form of search terms or filters. It is separated by a question mark (?) and includes key-value pairs.
Example: www.infidigit.com/search?query=SEO (Here, ?query=SEO indicates that the user is searching for SEO-related content on Infidigit’s website.)
Types of URLs
There are several types of URLs, each serving a unique purpose in how content is organized, accessed, and presented on the web. Understanding these types helps improve both user experience and SEO efforts, ensuring that URLs are optimized for clarity, searchability, and navigation.
Here are the main types of URLs:
- Absolute URL: An absolute URL provides the complete address, including the protocol, domain name, path, and additional details needed to access a resource.
- Relative URL: A relative URL points to a resource within the same website, omitting the domain name. It’s concise and automatically understood by the browser.
- Canonical URL: A canonical URL indicates the preferred version of a webpage to search engines, preventing duplicate content issues.
- Dynamic URL: Dynamic URLs contain parameters and query strings, often used for content that changes frequently or is generated by a database.
- Static URL: A static URL points to content that doesn’t change frequently, such as an informational page, making it simple and SEO-friendly.
- Shortened URL: Shortened URLs are compact versions of longer URLs, often used for sharing links on social media or in campaigns, and are created using URL shortening services.
Each type of URL has its own strengths and use cases, and understanding when to use each can help optimize the user experience and improve SEO performance.
What is the importance of URL structure in SEO?
A well-organized URL structure is essential for SEO because it helps search engines and users easily navigate and understand your website’s content. Here’s why URL structure matters for SEO:
User Experience
A well-structured URL enhances user experience by making navigation more intuitive. When users can easily understand the content of a page just by looking at the URL, they are more likely to click on it. URLs that are clear and descriptive provide a sense of trust and relevance, making users feel more confident in visiting your site.
Rankings
URL structure plays a key role in SEO rankings. Search engines prefer URLs that are simple, descriptive, and keyword-rich. Well-optimized URLs help search engines understand the content and context of a page, boosting its chances of ranking higher for relevant search queries.
Links
URLs are essential when it comes to linking both internally and externally. A clean, meaningful URL is more likely to be shared and linked to by others. Additionally, when building backlinks, URLs with relevant keywords are more likely to rank better and drive more traffic to your site.
Tracking in Analytics
URL structure is crucial for tracking website performance in analytics tools. Properly structured URLs with clear parameters allow for easy tracking of user behavior, traffic sources, and conversion metrics. This helps in analyzing the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and identifying areas for improvement.
Keep it Simple & Concise
Simplicity and brevity in URL structure are vital for both SEO and user experience. Short and straightforward URLs are easier for users to remember, type, and share. They also ensure that search engines can index and rank the pages more efficiently, making the website more accessible and user-friendly.
The best way to keep a URL structure clean is by making them SEO friendly. SEO friendly URL structure demands to follow a specific structure that could vary depending upon the type of a website. E.g.,
- For a blog, the structure could be:
https://www.domain.com/blog-name. If your blog has multiple categories, then it can be changed to: https://www.domain.com/category/blog-name. - For E-commerce, it could be:
https://www.domain.com/department/category/sub-category/product
where; dept = mens, womens, boy, girls, kids; category = top-wear ; sub-category = t-shirts ; product = black t-shirt
Today, the competition to rank at the top of Search Engine Results Page (SERPs) is higher than ever. Businesses heavily invest in Digital Marketing services and majorly into SEO services since the cost per lead is less than paid or other channels. Hence, while you take care of every technical aspect of a website, do not miss to consider the structure of the URL.
What are the common mistakes to avoid when structuring URLs for SEO?
A poorly structured URL can negatively impact both user experience and search engine rankings. Avoiding common mistakes ensures your URLs remain clean, readable, and SEO-friendly. Here are some key errors to watch out for:
- Using Long and Complex URLs – Lengthy URLs with unnecessary parameters make it harder for users and search engines to understand the page’s content. Keep URLs concise and relevant.
- Ignoring Keywords in URLs – Excluding relevant keywords can reduce a page’s SEO potential. Including a primary keyword helps search engines recognize the topic.
- Using Underscores Instead of Hyphens – Search engines like Google recommend using hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) to separate words in URLs for better readability.
- Including Special Characters and Numbers – URLs with symbols, numbers, or random characters appear unstructured and can confuse users. Stick to simple, readable words.
- Using Uppercase Letters – URLs are case-sensitive, meaning “Example.com/Page” and “example.com/page” can be treated as different pages, leading to duplicate content issues. Always use lowercase letters.
- Not Implementing Redirects After Changing URLs – Modifying a URL without setting up a proper 301 redirect can result in broken links and loss of SEO value.
- Overloading URLs with Subfolders – A deep directory structure (e.g., “example.com/category/subcategory/product/page”) makes URLs complex. Keep the structure as simple as possible.
- Using Generic or Auto-Generated URLs – URLs like “example.com/page?id=12345” are unclear and provide no context. Instead, use meaningful slugs like “example.com/best-seo-practices”.
By avoiding these mistakes, you can create an SEO-friendly URL structure that enhances your site’s ranking potential and user experience.
FAQ about URL & URL Structure
What is URL structure and why is it important for SEO?
A URL structure refers to the format and organization of a website’s URLs. It plays a crucial role in how users and search engines navigate and understand web pages. A well-structured URL improves SEO by making it easier for search engines to index content and for users to remember and share links. It enhances user experience, boosts click-through rates, and contributes to better rankings by ensuring URLs are clean, descriptive, and keyword-rich.
How does URL structure impact search engine rankings?
URL structure influences search engine rankings in several ways:
- Crawlability: A clear, organized URL helps search engines efficiently crawl and index pages.
- Keyword Relevance: URLs that include relevant keywords provide search engines with context about the page.
- User Experience: Simple, readable URLs encourage users to click, improving engagement metrics like dwell time and bounce rate.
- Link Sharing: Short, meaningful URLs are easier to share and link to, improving off-page SEO.
What are the best practices for creating SEO-friendly URLs?
To create an SEO-friendly URL structure, follow these best practices:
- Keep URLs short and descriptive (e.g., example.com/seo-tips instead of example.com/p=1234).
- Use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) to separate words for better readability.
- Include relevant keywords but avoid stuffing.
- Use lowercase letters to prevent duplicate content issues.
- Avoid special characters and dynamic parameters that can make URLs complex.
- Maintain a logical structure with clear categories if necessary (example.com/blog/seo-guide).
How can I improve my website’s URL structure for better SEO performance?
Improving your URL structure involves:
- Optimizing existing URLs by making them concise and relevant.
- Redirecting outdated or broken URLs using 301 redirects to maintain link equity.
- Using HTTPS for security and better rankings.
- Eliminating unnecessary parameters from dynamic URLs (example.com/page?id=123 should be example.com/product-name).
- Ensuring consistency across all pages for a well-organized site hierarchy.
What Is an API URL Structure?
An API URL structure defines how endpoints in an API are organized for ease of access and consistency. A good API URL structure follows RESTful principles, making it predictable and scalable. Example:
- Base URL: https://api.example.com/
- Resource Endpoint: https://api.example.com/users/ (to fetch user data)
- Query Parameters: https://api.example.com/users?id=123 (to fetch a specific user)
A well-structured API URL improves developer experience, ensures efficient data retrieval, and maintains logical organization in web applications.
Popular Searches
How useful was this post?
0 / 5. 0












1 thought on “Understanding URL Structure in SEO: Why It Matters for Your Website’s Success”
The good thing with URL structure is that you just have to set up things right once (for the bigger picture).
Then, just follow a simple list of best practices (which I’ll share with you soon) when creating new URLs.