Planning on building a new website, redesigning one, or making a major migration? The first concern you might have is zeroing in on the structure of your website for optimal search engine optimization.
There are two types of site structures that are widely used for websites, and the debate over which one is better has been long ongoing. We are talking about subdomain vs subfolders. How do they impact your SEO? How do they make your website more recognizable for search engines? Which one is the better option? Let us take a deep dive into the subdomain vs subfolder debate and identify which one comes out on top.
Understanding the Difference Between a Subdomain & Subfolder
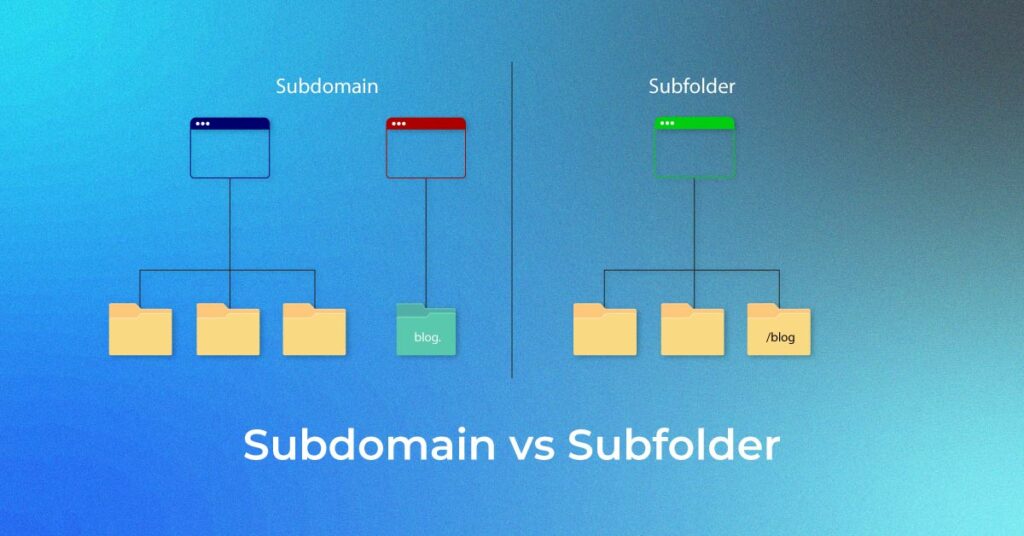
While subdomains and subfolders share similarities, they function differently and impact website structure and SEO in distinct ways.
A subfolder is a “child directory” within a parent directory, acting as a path under the main domain. For example, in example.com/blog, “blog” is a subfolder within the primary website. Since subfolders operate under the main domain, they inherit its authority, making it easier to consolidate SEO efforts.
A subdomain, on the other hand, is a separate content repository with its own unique URL, such as blog.example.com. Unlike subfolders, subdomains function independently and are treated by search engines as distinct websites, meaning they require separate SEO strategies.
Choosing between a subdomain and a subfolder depends on your website’s structure, goals, and SEO priorities. To make an informed decision, let’s take a closer look at what subdomains and subfolders are and how they function.

Unleash your website's potential by harnessing Infidigit's 400+ SEO audit to achieve peak site health & dominance on Google organic search.
Looking for an extensive
SEO Audit for your website?
Unleash your website's potential by harnessing Infidigit's 400+ SEO audit to achieve peak site health & dominance on Google organic search.

What is a Subdomain?
A subdomain is a separate domain created under a main website when businesses want to keep specific sections distinct from the root domain. These domains serve unique purposes, and Google treats them as independent websites, meaning they require separate SEO efforts.
Subdomains are commonly used for different functions, such as blogs, support pages, online stores, or regional websites. While they offer flexibility, they don’t automatically inherit the main domain’s authority, which can impact SEO.
Examples of Subdomains
Many well-known websites use subdomains to organize content effectively. For instance, Netflix has several subdomains, each serving a different purpose:
- help.netflix.com – Customer support
- dvd.netflix.com – DVD rental service
- blog.netflix.com – Official blog
- jobs.netflix.com – Career opportunities
By using subdomains, companies can create dedicated sections for different services while maintaining brand consistency.
How do subdomains look on a server?
As mentioned previously, Netflix has an array of subdomains, each operating as an independent entity that requires its own servers. In the early 2000s, the cost of operating separate servers and the memory space required for subdomains were very heavy on the pockets. But nowadays, with mobile-first indexing, the landscape of subdomains has changed. Subdomains are now mainly used for hosting mobile versions of your websites. For example, if your website is “www.abcd.com”, then its subdomain would look something like “m.abcd.com”.
Let’s assume that you want a subdomain to fill in contact forms from customers. Your subdomain for contacting would be m.contactabcd.com.
Businesses all across the globe use subdomains to host versions of their website in foreign languages or even for filing heavy data like big-sized downloadable resources or blogs.
When Should You Use a Subdomain?
-
Technical Reasons
Web developers often use a password-protected subdomain to host staging versions of websites for testing new templates, experimenting with the designs, and much more.
It is quite easy for developers to create a subdomain that replicates the main website. This is done by setting up a new database and installing a fresh version of the main website. Moreover, since this subdomain is not linked anywhere on the internet, search engine crawlers are not able to find it. Even if they do, these subdomains are password-protected, so the crawlers would not be able to do anything.
However, it can be tricky to use subdirectories to do the same, as there is a high possibility of major errors in the link structure that can be hard to navigate around.
Developers are more prone to using subdomains as it allows them to try multiple layout templates, designs, plugins, and other technologies without it having any effect on the main website.
-
Branding Reasons
It is always preferable for a brand to compartmentalize its various sections on a website. Further expanding on the Netflix example, they have a separate support domain for users where they can easily access resources like FAQs, guides, and other support materials.
-
SEO Considerations
There are many reasons why hosting a subdomain might prove to be useful for your website’s SEO. For instance, if you have a topic to publish that is in no way related to your main site, a subdomain is a perfect option to publish it on. This will isolate this new topic to its own URL away from your main website while still being related to your main website.
A very common example of this is news and media publishing websites hosting a subdomain for recipe content. It helps them separate the completely different content from their niche while still making it static and close to the brand.
Since Google sees subdomains as their own websites, publishing SEO-optimized content on them can significantly improve their rankings and give a boost to your brand’s reach. The subdomain can rank on its own and bring in newer demographics to your website for significant growth in organic traffic.
SEO Benefits of Using Subdomains
-
Do Subdomains Improve Rankings?
Subdomains work seamlessly in incorporating their own SEO rankings with the parent website. This can be especially helpful for brands that want to segregate their content within a multitude of niches and domains.
Since subdomains are seen as different websites on Google, they stand on their own in terms of ranking. However, internal linking on these subdomains can help Google in connecting the dots and improving the reach of your parent website. Moreover, this can also bring in organic traffic to your main website from the users going on these subdomains and getting engaged with the content. This will work towards improving your website’s rankings.
Google’s algorithms have evolved and are quite adept now in differentiating domains and subdomains. Hence, it is always a good sign to the algorithms if your subdomains generate good engagement and send users over to your main website.
-
How Subdomains Affect Link Equity & Authority
Subdomains function as separate entities from the main domain, which means they do not automatically inherit the authority or link equity of the root domain. Search engines treat subdomains as independent websites, requiring them to build their backlink profiles and SEO authority.
For example, if example.com has high domain authority, it won’t fully transfer to blog.example.com. While internal linking can pass some value, it’s less effective than using subfolders (example.com/blog).
This is why many businesses prefer subfolders for SEO-driven content, as they help consolidate authority and improve rankings. Choosing between a subdomain and a subfolder depends on your website’s structure and goals.
-
User Experience & Segmentation
Since most of the subdomains are used for unique purposes, they help segregate the various use cases of the users. Netflix does this by sending users to different subdomains made for different tasks, as discussed before.
Having multiple subdomains allows businesses to serve their users better. For instance, if someone is looking for payment support, Netflix’s subdomain for support has all the answers they would need instead of them having to go through various pages to find the answer they are looking for. Similarly, they have a subdomain for job openings, which only caters to this segment.
Using subdomains smartly can significantly enhance the user experience and help your users in navigating through anything related to your brand.
What is a Subfolder or Subdirectory?
A website has different sections for categories and web pages. These are often put into folders by developers, which are called subfolders or subdirectories. Think of it as file storage on your computer. You create different folders to organize different types of files on your desktop. A subdirectory works in the same way.
Subfolders have names similar to your desktop folders such as “/resume-templates”. This folder is where all the HTML pages for resume templates would go.
Subfolders are usually virtual on PHP-based websites and WordPress. They cannot be navigated through an FTP program since they don’t exist on the servers. However, they are still an important element for your website’s file structure.
In conclusion, a subfolder is an integral part of the website’s structure and is associated with your website’s domain name.
SEO benefits of using Subfolder
-
Link Equity
Link equity is an important ranking factor for search engines. Links traditionally should pass authority and value on a website from one webpage to another. This is determined by search engines when they refer to the thematic relevance, content quality, and relevance of the content linked. For this, search engines crawl the subfolders on a website comprehensively.
-
Increases domain authority
If your website has links from authoritative domains, it sends a signal to search engine algorithms that your content’s quality is good and a reliable source. This helps your website in increasing its domain authority. Since domain authority is a trailing metric and not a ranking factor, improving domain authority helps you get ahead of your competition on SERP rankings.
-
Ease of Management & Site Structure
Subfolders keep all content under the main domain, making it easier to manage and track within a single SEO strategy. Since everything is housed under one domain (example.com/blog), analytics, backlinks, and authority remain consolidated, simplifying SEO efforts. This structure also ensures that search engines crawl and index content more efficiently.
-
Branding Consistency
Using subfolders helps maintain a unified brand identity, as all content remains under the main domain. For example, example.com/store reinforces brand recognition better than store.example.com, which may feel like a separate entity. This consistency enhances user trust and strengthens domain authority, benefiting overall SEO performance.
Google’s Stance on Subdomains vs. Subfolders
John Mueller, a Senior Analyst and Google’s Head of Search Trends at Google noted that the subdomain vs subfolder argument was irrelevant, and Google’s algorithms process both in the same way. He said
“Google Web Search is fine with using either subdomains or subdirectories…use what works best for your setup and think about your longer-term plans when picking one or the other.”
However, this does not seem to be entirely true as there have been a lot of questions about whether Google’s algorithms process subdomains and subfolders the same way. So, which one should you choose for your website? Let us see the verdict.
When to Choose a Subdomain vs. a Subfolder?
Choosing between a subdomain and a subfolder depends on your website’s structure, SEO strategy, and business goals. While Google claims to handle subdomains and subfolders similarly, studies suggest that subdomains may not always pass authority and keywords as efficiently as subfolders. Let’s explore when to use each approach.
When Should You Use a Subdomain?
Subdomains are ideal when you need to create a distinct section of your website that operates independently. They help separate content that differs significantly from the main site, such as:
- Regional or multilingual websites (e.g., fr.example.com for French users)
- Support portals (e.g., help.example.com)
- E-commerce stores separate from the main site (e.g., store.example.com)
- Community forums or blogs that require different hosting or CMS
However, subdomains can present SEO challenges. Studies show that keywords on subdomains may not always contribute to the root domain’s rankings. Additionally, backlinks may funnel into subdomains instead of strengthening the main website. This fragmentation can dilute SEO efforts.
When Should You Use a Subfolder?
Subfolders (example.com/blog) keep all content under the main domain, helping search engines consolidate authority, backlinks, and keyword rankings. They are recommended for:
- Content marketing efforts, such as blogs (example.com/blog)
- Landing pages for campaigns
- Product pages that belong to the main website
Using subfolders improves analytics tracking and ensures that tools like HubSpot or Google Analytics can measure performance more effectively. Since all content remains within the primary domain, SEO value is retained and distributed efficiently.
Pros and Cons of Each Approach
Subdomains offer flexibility for managing distinct website sections separately, making them ideal for different services, regions, or platforms. However, since search engines treat them as independent sites, SEO efforts become fragmented, potentially weakening backlink strength and rankings.
Subfolders, on the other hand, keep content under the main domain, consolidating SEO value and making management easier. They help strengthen domain authority, improve search rankings, and streamline tracking. While subdomains work for specific use cases, subfolders are generally better for SEO, ensuring a unified and optimized website structure. The choice depends on your website’s needs.
Best Practices to Optimize Subdomains & Subfolders for SEO
Whether using subdomains or subfolders, optimizing them correctly ensures better search visibility and performance.
- Maintain a clear site structure – Ensure easy navigation and logical hierarchy.
- Use internal linking strategically – Connect relevant pages to distribute authority.
- Optimize URLs – Keep them short, descriptive, and keyword-rich.
- Ensure proper indexing – Use XML sitemaps and robots.txt to guide search engines.
- Implement consistent branding – Maintain uniform design and messaging across all sections.
- Monitor performance – Track rankings and traffic using tools like Google Search Console and Analytics.
By following these best practices, you can maximize the SEO benefits of both subdomains and subfolders.
FAQ
What is a subdomain, and what is a subdirectory in website structure?
A subdomain is a separate section of a website designated by a prefix, such as “blog.example.com,” while a subdirectory is a folder within the main domain, like “example.com/blog.”
How does choosing between a subdomain and a subdirectory impact SEO?
The choice can significantly impact SEO. Search engines treat subdomains as separate entities and subdirectories as part of the main domain. This influences factors like domain authority and site structure.
When should I use a subdomain for my content?
Use a subdomain when the content is entirely different in theme, purpose, or target audience from the main domain. For example, if you want to host a separate blog or e-commerce store.
When is it better to use a subdirectory for organizing content?
Use a subdirectory when the content is closely related to the main domain and shares a common theme or topic. This approach is often preferred for maintaining a unified site structure.
How does using subdomains affect the SEO authority of my main domain?
Subdomains are generally treated as separate entities by search engines. This means they won’t directly contribute to the SEO authority of the main domain, potentially spreading your SEO efforts thin.
Does Google treat subdomains as separate websites?
Yes, Google views subdomains as separate websites, requiring independent SEO efforts. While it recognizes their connection to the main domain, subfolders are generally preferred for consolidating authority and improving rankings.
Can I switch from a subdomain to a subdirectory without losing SEO rankings?
Yes, but proper execution is key. Use 301 redirects, update internal links, sitemaps, and canonical tags, and monitor performance in Google Search Console. Though rankings may fluctuate initially, a well-managed migration can strengthen SEO by consolidating authority under the main domain.
Conclusion
Your website should be the most profitable employee in your organization, and it’s always better to take the help of an SEO company like Infidigit to get the job done. Having experts who know the ins and outs of both subfolders and subdomains, we can help you in making full use of both, and significantly enhance your website’s SEO. Contact us to know more.
Popular Searches
How useful was this post?
0 / 5. 0













2 thoughts on “Subdomain vs. Subfolder – Which One is Best for SEO?”
I like your post a lot I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I’ve enjoyed browsing your posts. I will subscribe to your feed, and I look forward to reading your next post.
We are glad that you liked our post. Check out our latest posts for more updates.